Version: Next
使用注解开发
面向接口编程
解耦,可拓展,提高复用,分层开发中,上层不用管具体的实现,大家都遵循共同的标准,使得开发变得容易,规范性好。
关于接口的理解
- 接口从更深层次的理解,影视定义(规范、约束)与实现(名实分离的原则)的分离
- 接口本身反映了系统设计人员对系统的抽象理解
- 接口应有两类:
- 对一个个体的抽象,它可对应为一个抽象体(Abstract class)
- 对一个个体某方面的抽象,即形成一个抽象面(Interface)
- 一个个体可能有多个抽象面,抽象体与抽象面是有区别的
三个面向区别
- 面向对象是指,我们考虑问题时,以对象为单位,考虑它的属性和方法
- 面向过程是指,我们考虑问题时,以一个具体的流程(事务过程)为单位,考虑它的实现
- 接口设计与非接口设计是针对复用技术而言的,面向对象(过程)不是一个问题。更多的体现就是对系统整体的架构。
使用注解开发
新建模块mybatis05, 重新导入父工程pom.xml,拷贝所有配置文件,拷贝实体类、工具类、接口 不再需要mapper.xml
接口+注解
@Select("select * from user")List<User> getUsers();核心配置文件中配置mappers标签
<mappers><mapper class="com.bsx.dao.UserMapper"/></mappers>测试类
@Testpublic void testAnnotationGetUsers() throws IOException {String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";InputStream inputStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(inputStream);SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();try {UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);List<User> users = mapper.getUsers();for (User user : users) {System.out.println(user);}} catch (Exception e) {e.printStackTrace();} finally {sqlSession.close();}}
本质:反射机制实现
第层:动态代理
实现CRUD
可以在工具类创建的时候实现自动提交事务(一言不合看源码)
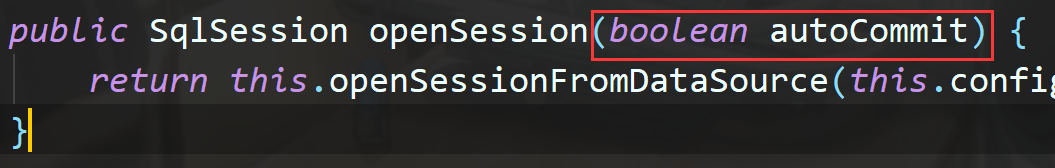
在创建sqlSession时,传入一个dtrue就行了
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
- 接口
给接口形参中为基本类型的参数,全部加上@Param("xx")注解
@Select("select * from user where id = #{id} and name = #{name} ")
User getUserById(@Param("id") int id, @Param("name") String username);
- 测试类
@Test
public void testAnnotationGetUserById() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
//传一个true开启自动提交事务
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
try {
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = mapper.getUserById(1, "改名的");
System.out.println(user);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
添加
- 接口
@Insert("insert into user(id, name, password) values (#{id},#{name},#{password})")
int addUser(User user);
- 测试
@Test
public void testAnnotationAddUser() throws IOException {
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream("mybatis-config.xml");
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder().build(resourceAsStream);
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession(true);
try {
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
User user = new User();
user.setId(5);
user.setName("注解来的");
user.setPassword("123");
int resultNum = mapper.addUser(user);
System.out.println("结果数字 = " + resultNum);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
sqlSession.close();
}
}
修改
接口
@Update("update user set name = #{name}, password = #{password} where id = #{id}")int updateUser(User user);
删除
接口
@Delete("delete from user where id = #{id}")int deleteUser(@Param("id") int id);
关于@Param()注解
- 基本类型的参数或者String类型需要加上它
- 引用类型不需要加
- 如果只有一个基本类型的参数,可以忽略,但是建议加上
- 我们在sql中引用的就是该
@Param("xxx")设置的xxx
#{} 和 ${}的区别
#是preparedStatement()防止sql注入$可能sql注入,能用#就用#