Version: Next
串——Sequence
- 字符串:由若干个字符组成的有限序列
- 字符串
world的前缀(prefix)、真前缀(proper prefix)、后缀(suffix)、真后缀(proper suffix)
概念 内容 前缀 w、wo、wor、worl、world真前缀 w、wo、wor、worl后缀 world、orld、rld、ld、d真后缀 orld、rld、ld、d
串匹配算法
- 查找一个
模式串(Pattern)在文本串(Text)中的位置例String text = "Hello World";String pattern = "or";text.indexOf(pattern); // 7 `or`包含在 text中,且从text的下标 7 位置开始text.indexOf("other"); // -1 `other` 不能存在与 text 中,因此返回 -1
经典串匹配算法
- 蛮力(Brute Force)
KMPBoyer-MooreRabin-KarpSunday
术语
tlen:text length的缩写,表示文本串 Text的长度plen:pattern length的缩写,表示模式串 Pattern的长度
蛮力——Brute Force
- 以字符为单位,从左到右移动模式串,直到匹配成功
- 只要模式串中的任意一个字符匹配失败,就将模式串在文本串中的位置移动
1
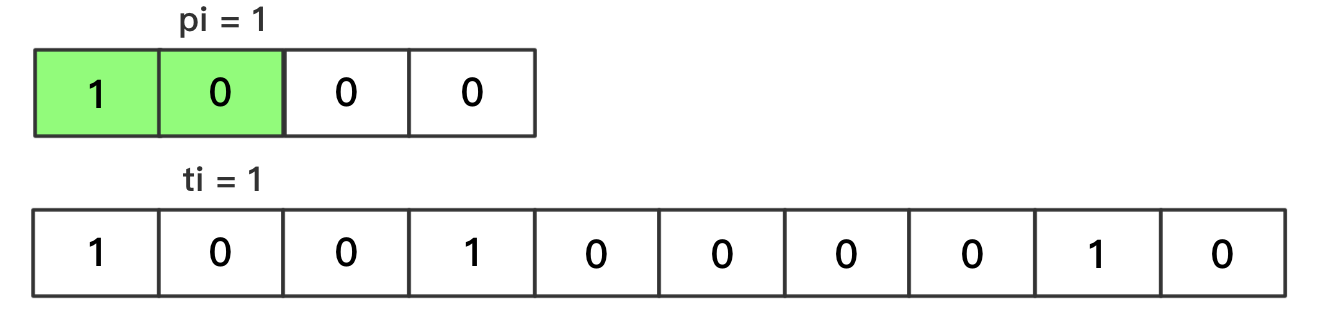
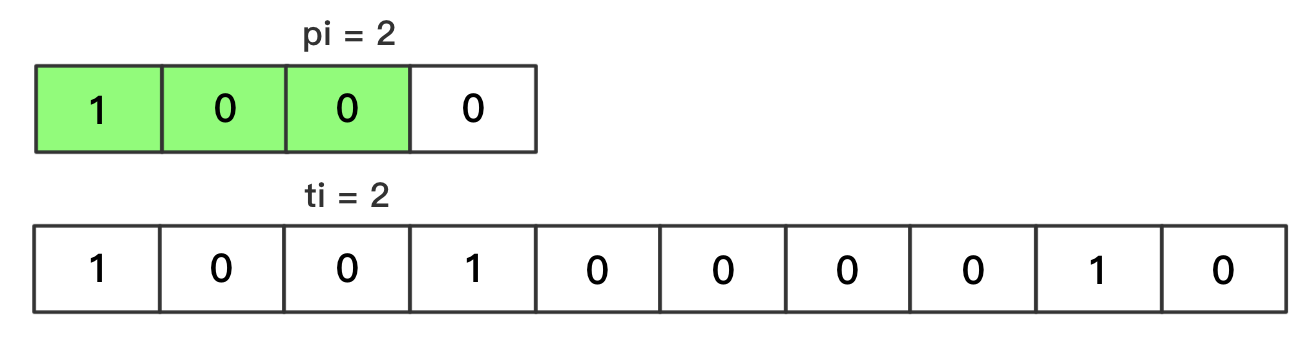
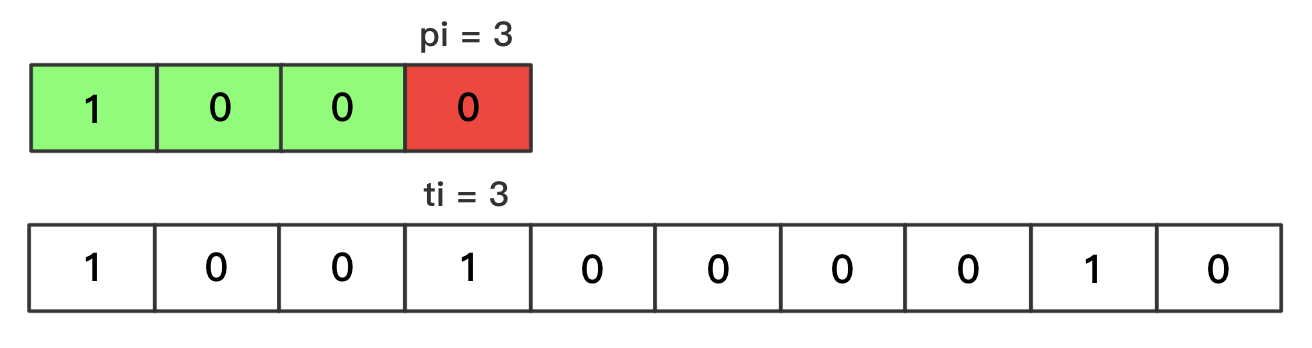
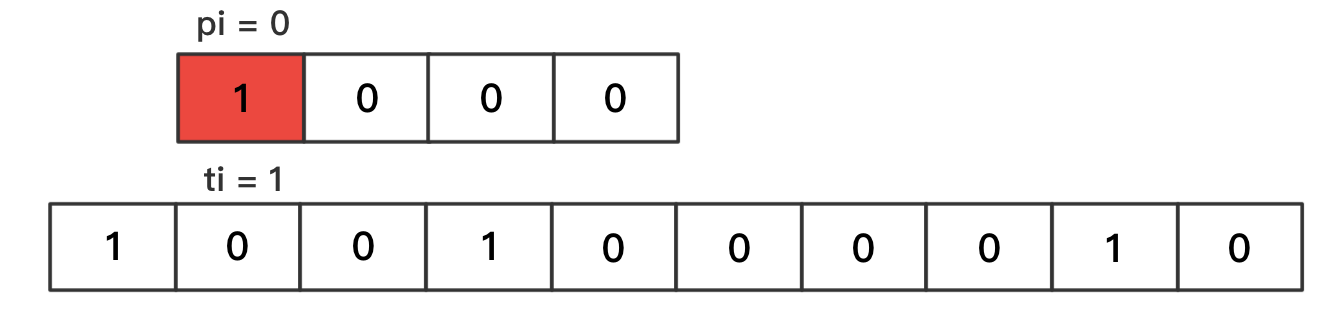
蛮力1——执行过程
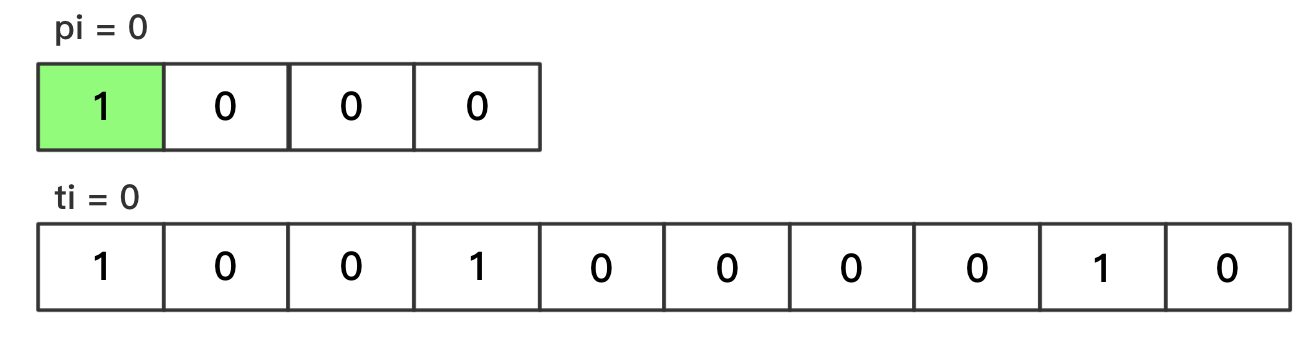
pi、ti分别表示模式串、文本串中,正在参与比较的字符的下标索引pi的取值范围为[0, plen)ti的取值范围为[0, tlen)匹配成功——单个字符
pi++、ti++匹配失败
- 跳到文本串的下一个字符开始比较,公式为
ti -= pi - 1(ti 向左移动先前匹配成功字符的长度,由于跳到文本串的下一个字符,所以还要加1);并且pi归零最终——完全匹配
- 当
pi = plen时,代表匹配成功- 显然应当返回:
ti - pi,为模式串起始字符在文本串中对应的下标
蛮力
/**
* 串匹配——蛮力1
*/
public class BruteForce01 {
public static int indexOf(String text, String pattern) {
if (text == null || pattern == null) return -1;
char[] textChars = text.toCharArray(); // 转成字符数组
char[] patternChars = pattern.toCharArray();
int tlen = textChars.length;
int plen = patternChars.length;
// 如果模式串长度大于 文本串长度 返回 -1
if (tlen == 0 || plen == 0 || plen > tlen) return -1;
int pi = 0, ti = 0;
while (pi < plen && ti < tlen) {
if (textChars[ti] == patternChars[pi]) {
pi++;
ti++;
} else {
ti -= pi - 1;
pi = 0;
}
if (pi == plen) return ti - pi;
}
return -1;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int res1 = indexOf("Hello World", "or"); // expect 7
int res2 = indexOf("Hello World", "abc"); // expect -1
System.out.println("res1 = " + res1);
System.out.println("res2 = " + res2);
}
}
执行结果
res1 = 7
res2 = -1
显然蛮力法的效率是很差的
- 接下来介绍
KMP