160.相交链表
类似题目
- 面试题 02.07 链表相交
- 面试题 52 两个链表的第一个公共节点
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
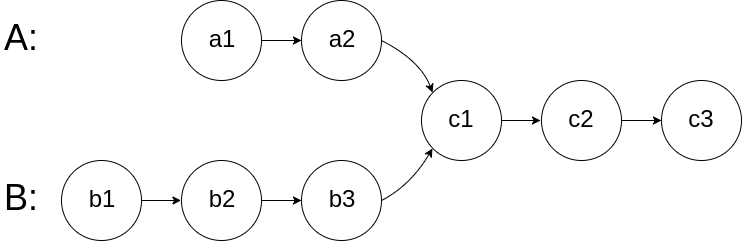
如下面的两个链表:
在节点 c1 开始相交。
示例 1:
输入:intersectVal = 8, listA = [4,1,8,4,5], listB = [5,0,1,8,4,5], skipA = 2, skipB = 3 输出:Reference of the node with value = 8 输入解释:相交节点的值为 8 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [4,1,8,4,5],链表 B 为 [5,0,1,8,4,5]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 2 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点。
示例 2:
输入:intersectVal = 2, listA = [0,9,1,2,4], listB = [3,2,4], skipA = 3, skipB = 1 输出:Reference of the node with value = 2 输入解释:相交节点的值为 2 (注意,如果两个链表相交则不能为 0)。从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [0,9,1,2,4],链表 B 为 [3,2,4]。在 A 中,相交节点前有 3 个节点;在 B 中,相交节点前有 1 个节点。
示例 3:
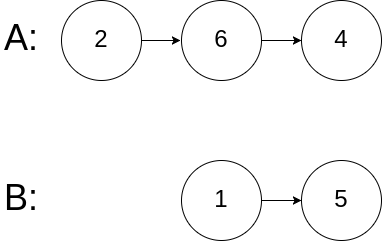
输入:intersectVal = 0, listA = [2,6,4], listB = [1,5], skipA = 3, skipB = 2 输出:null 输入解释:从各自的表头开始算起,链表 A 为 [2,6,4],链表 B 为 [1,5]。由于这两个链表不相交,所以 intersectVal 必须为 0,而 skipA 和 skipB 可以是任意值。 解释:这两个链表不相交,因此返回 null。
注意:
如果两个链表没有交点,返回 null. 在返回结果后,两个链表仍须保持原有的结构。 可假定整个链表结构中没有循环。 程序尽量满足 O(n) 时间复杂度,且仅用 O(1) 内存。
160. Intersection of Two Linked Lists
难度简单1072
Given the heads of two singly linked-lists headA and headB, return the node at which the two lists intersect. If the two linked lists have no intersection at all, return null.
For example, the following two linked lists begin to intersect at node c1:
It is guaranteed that there are no cycles anywhere in the entire linked structure.
Note that the linked lists must retain their original structure after the function returns.
Example 1:

Example 2:

Example 3:
Constraints:
- The number of nodes of
listAis in them. - The number of nodes of
listBis in then. 0 <= m, n <= 3 * 1041 <= Node.val <= 1050 <= skipA <= m0 <= skipB <= nintersectValis0iflistAandlistBdo not intersect.intersectVal == listA[skipA + 1] == listB[skipB + 1]iflistAandlistBintersect.
Follow up: Could you write a solution that runs in O(n) time and use only O(1) memory?
哈希表法
- 把 A 链表的所有节点的引用都存入一个 HashSet
- 遍历 B 链表,检查 A 的 HashSet 中是否包含 B 中节点
- 时间复杂度 O(M + N)
- 空间复杂度 O(n)
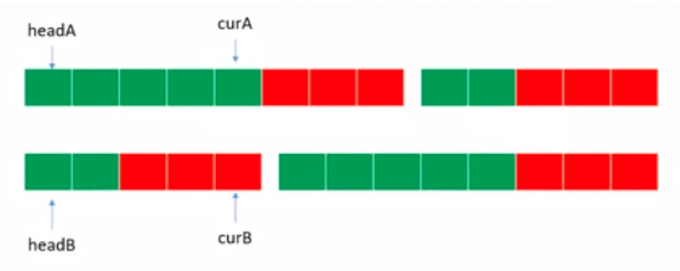
双指针法
- 两个链表分别拼接彼此,形成 2 个新链表,两个新链表的尾部是相同的
- 即可两个指针同步遍历链表,比较堆地址找出相交节点
- 注意两个链表没有相交节点的情况